1. Micro-Electrolysis Filler
Micro-electrolysis filler, also known as iron-carbon filler, is a core component for wastewater treatment via micro-electrolysis. Standardized iron-carbon filler is synthesized by fusing multi-metal alloys with catalysts at 1300°C, effectively resolving issues like passivation and compaction. During wastewater treatment, it generates a 0.9–1.7V potential difference, forming numerous microscopic galvanic cells within the reactor. Using wastewater as the electrolyte, these cells enable electrochemical degradation of organic pollutants through redox reactions at the anode and cathode.
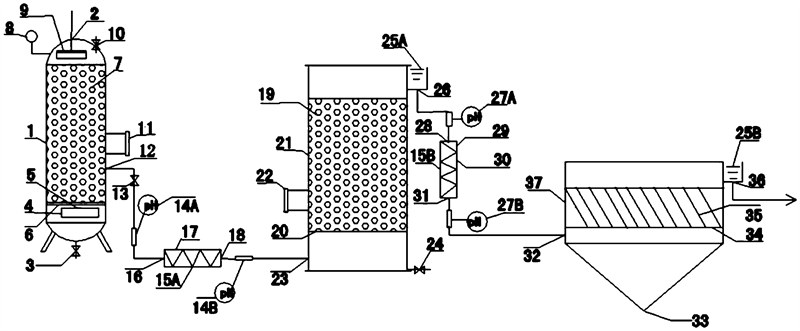
2. Technology Overview
Iron-carbon micro-electrolysis leverages three synergistic mechanisms:
Iron’s reducibility
Electrochemical properties
Flocculation/adsorption by iron ions
Materials: Typically cast iron scraps mixed with activated carbon/coke. When immersed in industrial wastewater (e.g., coking or electroplating effluent), dual electrolysis occurs:
Internal: Microscopic cells form between iron carbide (cathode) and pure iron (anode) due to their redox potential difference, releasing Fe²⁺ into the solution.
External: Macroscopic cells develop between iron scraps and surrounding carbon, enhancing reactivity. Catalysts may be added to amplify the potential gradient.
Key Reactions:
Anode (Fe):
Fe−2e−→Fe2+E∘(Fe/Fe2+)=0.44V
Cathode (C):
2H++2e−→H2E∘(H+/H2)=0.00V
Highly reactive nascent Fe²⁺ and atomic H degrade organic compounds via chain cleavage or ring opening.
With Aeration:
O2+4H++4e−→2H2OE∘=1.23V
O2+2H2O+4e−→4OH−E∘=0.41V
4Fe2++O2+4H+→2H2O+4Fe3+
Generated Fe³⁺ hydrolyzes into polymeric Fe(OH)₃ flocculants, which adsorb suspended solids/heavy metals more effectively than conventional coagulants.
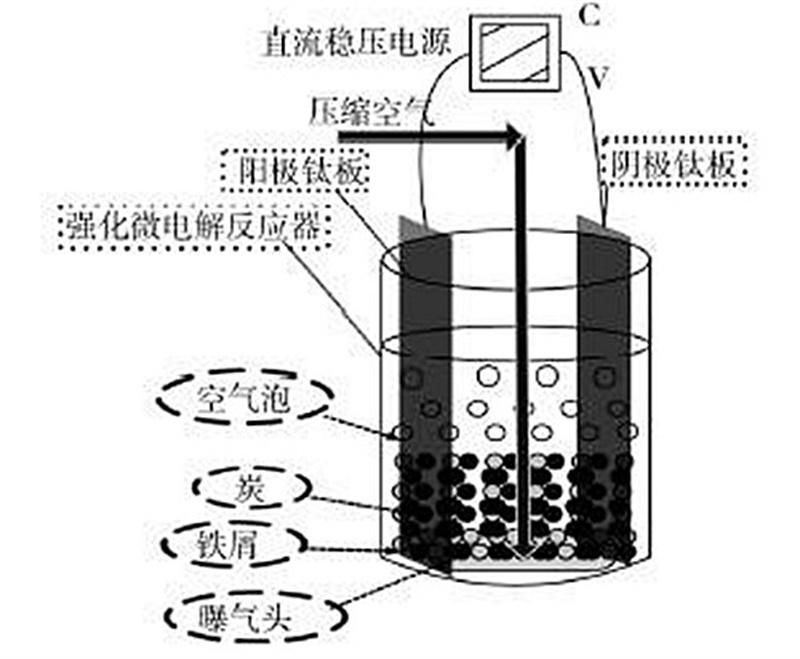
3. Technology Advantages
Rapid reaction (30 mins–few hours for most industrial wastewater).
Broad applicability: Degrades recalcitrant organics (e.g., azo dyes, nitro/halogen compounds).
Cost-effective: Simple operation, minimal maintenance, and stable performance. Fillers require periodic replenishment without replacement/activation.
In-situ coagulation: Fe²⁺/Fe³⁺ ions outperform chemical coagulants, eliminating secondary pollution.
High removal rates for COD/color while improving biodegradability (B/C ratio).
Multi-pollutant removal: Phosphorus precipitation and heavy metal reduction.
Flexible integration: Suitable as pre-treatment for high-concentration wastewater or post-biological polishing.
Enhanced sludge settling and biofilm formation in biological systems.
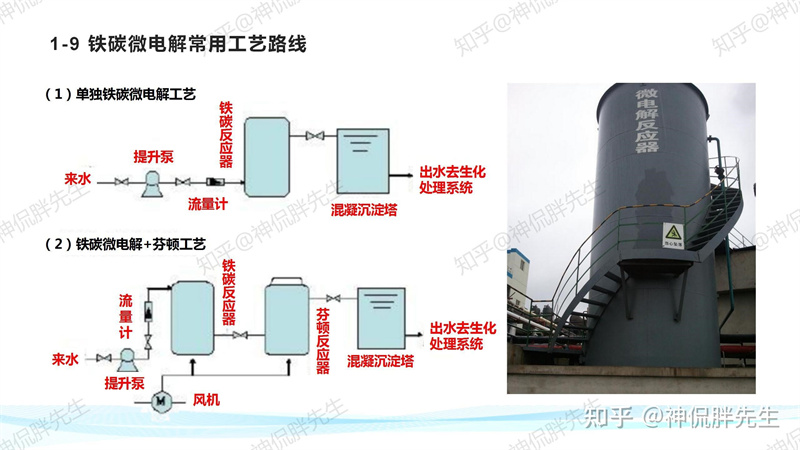
4. Applications
Ideal for high-COD, toxic, colored, and bio-resistant wastewater, including:
Industries: Textile, chemical, electroplating, pulp/paper, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, etc.
Key improvements:
Dyeing/printing effluents: Significant COD/color removal + B/C ratio boost.
Petrochemical/leather wastewater: Enhanced biodegradability.
Heavy metal-laden streams (mining, electroplating): Effective metal removal.
Organochlorine/phosphorus pesticides: Degradation + sulfur/phosphorus elimination.



